I’ll post the translations to be able to read it all in one go here. Seems like some of the translation is a little off…
VST System Link
The idea of the separation of “work” between multiple computers in a virtual studio hovers a long time. How often one car load “eyeballs” - she and multi-track recorder and mixer, synthesizer and sampler, effects processor and at the same time! Stands in a large project to add a couple of new audio tracks - and no longer “pull” virtual tools necessary to transform their MIDI-tracks in the audio. It is necessary to sort out with the audio tracks - the disc begins to choke, it is necessary to do an intermediate reduction (baunsing). It is necessary to “hang” more intensive plug-ins, and work in real-time becomes impossible. We have to solve the problem mathematically, recalculation of the entire project is offline. Even a machine with two processors dvuhgigagertsovymi ever say yes “can not.”
Facilities work on a single machine is also not a lot of - a lot of open panels of virtual instruments and plug-ins, editing windows MIDI- and audio parts, and even a stand-alone software synthesizer with the control panel sound card …
In general, the creators of the virtual studio said “enough.” And offered to the public a new technology - VST System Link, designed to solve the problem.
In this technology, several computers networked together, whereby the load on each computer is reduced and the total computing power of the system increases. It does not require network cards, hubs, network cables, and other attributes, which is usually associated the word “network”. All that is needed from the hardware devices - are computers, sound cards with digital interface virtually any format (SPDIF, AES / ESU, ADAT, TDIF) and digital cables. It is clear that the interfaces must be compatible formats. Each board must have drivers ASIO, and on each computer on the network must be installed that supports the VST System Link. At the time of writing such programs, in addition to Cubase SX, Nuendo were 1.6 and up, as well as a special version of Cubase 5.1 (System Link version).
Another firm Steinberg recommends using switches “keyboard - graphics adapter - mouse” (KVM switchbox). With such a switch can be used with several computers one keyboard, mouse and monitor. These devices are inexpensive, but it is much easier to work, especially at home, where sometimes one computer monitor is not enough space. Most importantly - do not need to buy for each computer full of “gentleman’s set” enough to have input-output devices in a single copy.
Advantages of the technology VST System Link from the engineering point of view is clear - every computer on the network performs its specific task. One works as a multi-track recorder or mixer, the second - as an effects unit, the third may be a synthesizer or sampler, and so on. Variations on this theme are endless, but in general, it looks as if running a complex of self-contained units, both in the physical studio. Most importantly, the entire system performs synchronization and positioning accuracy of the sample, without the use of additional external devices and special sound cards that can read and generate timecode.
In addition, VST System Link technology is platform-independent. For example, you can work together the Mac and PC. You get the benefits of both platforms, and decide what kind of problem it is convenient to charge for your particular operating system. And it happens that there is a wonderful plug-in for Mac, which is not for the PC, and vice versa. Online VST System Link is not a problem. Also addressed the issue and performance machines. If you have an old computer that is good at playing multiple audio tracks, you can use it as a recorder, and a more powerful computer to give completely under software synthesizers and effects processors. If the project requires a large number of audio tracks, you can assign them to different machines, organizing virtual RAID-array. I think the possibility of such a dynamic redistribution of functions depending on the needs - one of the main advantages of the technology.
VST System Link network has a ring topology: Digital output cable is connected to the first computer with a digital input of the second output of the second - with the input of the third, and so on (see Fig. 17). Output of the last computer is connected to the input of the first to complete the circuit. Number of channels on each network segment is not limited and depends on the number of inputs and outputs have a sound card, as well as the number of audio channels per single input / output. It is clear that multi-channel ADAT and TDIF interfaces allow you to create a more advanced network, and much less effort than interfaces SPDIF and AES / EBU.
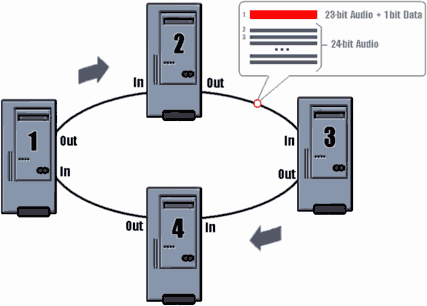
Signals are transmitted over a network of several types: digital audio with embedded sync (self-clock), positioning data, traffic management team and, of course, MIDI-messages. Without them control synthesizer or sampler from another machine possible. By the way, the developers promise a much higher fidelity rhythmic MIDI-events than any other software and hardware solution based on the MIDI-interfaces.
VST System Link protocol does not require the use of a separate Word Clock signal from any of the generator and the corresponding jacks on the sound card. Throughout the network are assigned to one charge, the generator which will produce a “shred” for all other boards and “knead” it, along with digital audio on a single cable. So that one board is the master and all other work in the external synchronization mode of the digital audio. However, in large networks firm Steinberg still recommends the use of synchronization Word Clock. I will assume that such synchronization is needed even for three computers. After each board generates its own internal clock, which is based on the incoming clock signal, and this can cause jitter and digital errors. With the passage of the signal through a series of cards on a ring network jitter should still increase.
To sync Word Clock synchronizer is better to use an external or digital mixer. In this case, all the boards should work in slave mode (on some boards, this is called AutoSync) and “listen” to the clock signal at the input to Word Clock or ADAT-cable.
Audio data transmitted by digital cable in a conventional manner, and to transmit all other types of signals using one bit of one of the audio channels. For example, when connecting two computers ADAT-cable turns seven channels of 24-bit audio, and one - 23-bit. Specialists of the company Steinberg argue that nothing wrong with 23-bit sound, no, because the dynamic range is still huge - about 138 dB. With this should agree, especially considering the fact that the majority of 24-bit analog-to-digital converters output a signal with the actual word length not exceeding 22 bits.
With regard to the transfer of MIDI-messages, for this purpose, the user can assign up to 16 ports of 16 channels each, for a total of up to 256 channels. Common sense dictates that convey all that stuff together with managers and service teams, one bit of one of the audio channels will be virtually impossible. But there is a way - the technology allows you to fully pay the “network” under the audio channel and MIDI-control information.
This also brings up the issue of the waiting time at the network. It will be equal to the sum of delays for each board. Although the accuracy of the synchronization waiting time does not affect (all VST-compatible software compensate for its recording and playback), when a large number of computers and large sizes ASIO-buffers work will become very uncomfortable. Technology developers are recommended to specify a buffer size for each board to delay it did not exceed 12 ms. The easiest way to find the optimal delay time by experimentation, reducing it until stability has not yet violated the network. In order to reduce the waiting time for monitoring the signal from the other computers, you need to enable ASIO Direct Monitoring (if it is supported by a sound card).
VST System Link: practice
Let us consider a few examples. First - the easiest option when there are two computers. The first step is to physically connect two sound cards. Let us boards are connected by ADAT-interface. Connecting the optical cable from the output of the first computer to the input of the second. Connect a second cable from the output of the second computer to the input of the first (see Fig. 18).
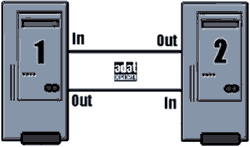
The next stage - the choice master card at Cloquet which will operate the entire system. On both computers, open the window Device Setup, where under VST Multitrack choose native ASIO-driver is supplied by the manufacturer (and not the type of driver ASIO Multimedia and ASIO DirectX, supplied with Cubase SX). Push button Control Panel. In Control Panel, set up a board clock source. On one computer the card to the external synchronization mode (this mode can be called “AutoSync”, “SPDIF In” and so on. N.), On the other - in the synchronization of the internal clock (“Master”, “Internal”, and so on. N .). If done correctly, the control panel should appear subordinate to the board information that enters a valid reference signal and a charge on it synchronized.
The next step - the harmonization of the project. Do projects on both machines have the same sampling rate and pace. Then - activation of the input ports and output buses, which organized the two computers (selection in the windows VST Inputs and VST Outputs, respectively). It is clear that at least on one of the boards should be secondary audio (and activated bus) for monitoring. We should also look at the control panel board, section switching inputs and outputs (or petchbey) and make sure that output bus allocated for the network connected to the desired digital output and digital input is activated.
Check the correctness of the resulting switching system can be very simple. Import one of the first computer audio tracks and start playing in a loop. Yield track should be sent to the bus through which data is transmitted by the second computer. The draft of the second computer also create an audio track and set for her “network” input port. When you turn on monitoring for this track should have begun to move the level indicator that tells me when the digital sound from the first computer. If works well feedback (ie, the second computer plays the sound, and gets his first input), then you can proceed to the main point.
We go out the window Device Setup (Fig. 19) and select the section VST System Link. In the fields of ASIO Input and ASIO Output select the input and output channels for the transmission of data over the network (it will go on a 23-bit audio), and then activate “workstation” by checking the Active. The same is done on a second computer.
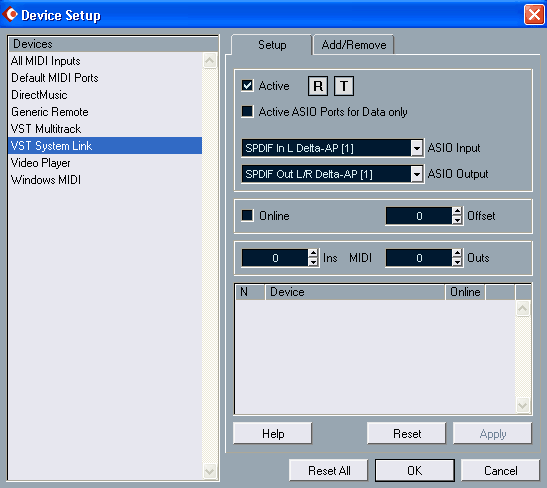
Once the second computer is activated, the bulb will flash “R” (Receive) and “T” (Transmit), and in the list at the bottom will names workstations (see Fig. 20).
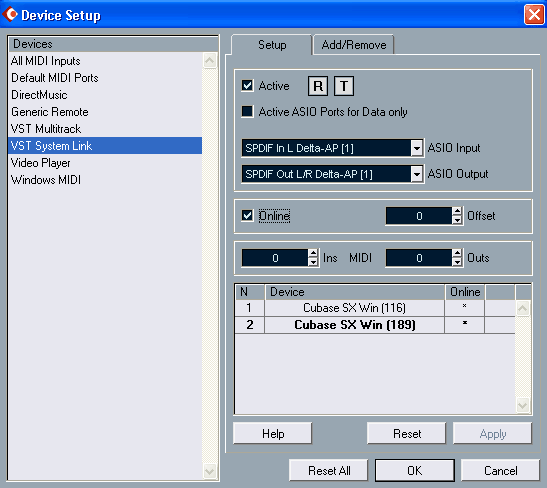
The name suggests, refers to any computer platform and what the program that supports the VST System Link, it works. For official purposes to each computer on the network is assigned a unique number (almost like IP-address in real networks). Name of the computer you are working on at the moment, is in bold. For convenience, you can change the name to something more readable.
Everything mentioned earlier, can be compared with the configuration software and network protocols to connect a computer to the Internet. But to enter the network only after activation of the remote connection. Activation in the VST System Link network runs mark options Online, located just above the list. Once the computer has been translated to “online”, it starts to get timecode and transport team. In the “offline” computer becomes independent from the others and is not involved in the transfer of data over a network, although it remains on the list. Choose to play in this mode it is possible only with his own transport panel.
A characteristic feature of Network System Link - there is no “server” or the master of the computer from which you can manage the rest. From any computer that is online, you can start playing or move to a point in the project, all the other machines.
Offset parameter in front of the option Online can be confusing. What else shift if promise sync up to the sample? The developers say that some sound cards behave so that the computer on the network is beginning to play a few samples earlier or later than others. However, do not say what kind of board …
Now another example. Let the first computer will be MIDI-sequencer and multitrack tape recorder, and the second - a virtual rack with two VST-instruments. In the VST System Link Device Setup window on both computers are specified by two input-output MIDI-port (field Ins and Outs). Once done, the MIDI-ports on both computers should appear two new: System Link 1 and System Link 2. On the first computer output of the MIDI-tracks direct to the port of System Link 1 (for one synthesizer), exit left - the port System Link 2 (second synthesizer). On the second computer, create the same number of MIDI-tracks, assign them to the appropriate network inputs as well as output ports, select VST-Instruments. When you turn on the computer monitor to the second track will begin accepting MIDI-messages and transmit them to the first virtual instrument.
As mentioned earlier, when a large number of events on several MIDI-ports per bit network channel may not be enough. In this case, will have to pay under a MIDI channel (prohibiting the transfer of audio on it). All you need - is to enable the option Active ASIO Ports for Data only.
Finally, we make a second computer with a virtual rack effects processors. To do this, create a separate effect of each stereo track, and the plug put in the gap of the track. The input port of a track, select one of the network and enable monitoring. On the first computer to select the track you want to process the effect, and the Inspector will send one of the promises on the fieldbus. A signal will be sent from the first computer to the second and processed without using CPU first.
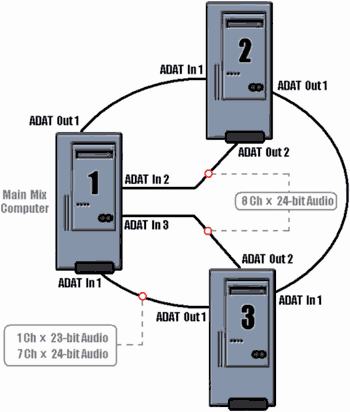
If your network consists of three, four or more computers, and sound cards have multiple digital inputs and outputs, the developers recommend the use of a mixed topology (ring plus star). In this case, the chain is only transmitted control information, and the sound on your computer mixer - directly through the available inputs and outputs. The figure shows the situation in relation to the cards with ADAT-interface (see Fig.
VST System Link: testing
Well, on paper it looks nice, but in reality? At the time of writing this article I had on hand two computers and three sound cards, which I decided to try out the new technology in action.
The configuration of the first computer: Pentium IV processor with a clock speed of 1.6 GHz, 512 MB of RAM, motherboard ASUS P4 TE, SCSI-controller Adaptec 29160, hard drive IBM DDYS of 36 GB video card Matrox Millenium G550, the operating system Windows XP Professional .
The configuration of the second computer: Pentium III processor with 550 MHz, 256 MB RAM, motherboard ASUS P3B-F, SCSI-Controller Tekram DC-390U / F, hard drive Seagate ST39175LW capacity 9.1 GB graphics card ASUS AGP-V3800 , the operating system Windows XP MUI.
Soundcard: Creative SB Live! Platinum, Midiman Audiophile 2496 and Aardvark Direct Pro LX 6. All boards have the same electrical interface SPDIF.
About the board Creative SB Live! from doubt, as officially released ASIO-drivers it has. I would not have to include it in the test at all, if it had not found a debug version of the alternative driver, developed by our compatriot Evgeny Gavrilov (kxproject.spb.ru). In this version, the author promises “Full ASIO support”. I thought - and you never know, suddenly earn? And installed alternative drivers.
However, an attempt to activate the card for the network failed. He had only to check the option Active under VST System Link window Device Setup, as after a brief rustling disk computer entered a state of hibernation, and after five or six seconds of silence Cubase SX with a bang “took off.” Such a reaction program was observed on both computers, so it was concluded about the unsuitability of the board Creative SB Live! for networking VST System Link (at least at its current implementation of alternative drivers).
The remaining two cards were distributed as follows: on a more powerful computer - Direct Pro LX 6 on less powerful - Audiophile. After a series of test boards in computers changed places, but the overall picture is not affected.
So, in order.
Digital inputs and outputs are switched on both boards were interconnected by two digital cables. Then a test was conducted on the correct switching as it was described in the previous section. Audio data is successfully transferred between computers as in the case when there was a charge generator shred Audiophile, and in the case where a tuft generates fee LX 6. In both boards was enabled ASIO Direct Monitoring.
Finally, the attempt was made to activate the network. First, the leading prescribed fee LX 6, and the fee Audiophile converted into sync mode input SPDIF. When enabling Active on both computers in the VST System Link flashes R and T, and in the list of active workstations, there are two computer rooms with 116 (LX 6) and 189 (Audiophile). However, when you try to charge a leading Audiophile entire network falling apart. Once in the control panel to select the internal oscillator Audiophile shred, and the fee LX 6 is put on external synchronization, both computers disappeared from the list.
Further testing was carried out in only one version running with the leading pay-LX 6. Since there were only two available transmission channel, the weaker computer to act as an auxiliary mixer, which brings several audio tracks. On two network channels pivoted material falling on a more powerful computer, where it is mixing with other audio tracks. Listening was carried out on two speakers, the first system is wired to the outputs Audiophile, the second - to the monitor output LX 6.
When you start playing on one of the computers on the second computer started instantly. Then listens for the same track simultaneously through both boards (in order to determine the presence of delay). To do this on the host computer drowned out all the tracks except the network, and the network was converted into monitoring mode. Delay of the hearing could not be determined, there was even a light flanger. Monitors played as if they were connected to the same amplifier with four outputs.
However, all the amenities on this and over. From time to time synchronization is broken, and one of the computers took off from the network. Establish any pattern in this process did not succeed. Sometimes there were more strange things. Starting with the computer where it was installed board Audiophile, the project played a few bars, and then spontaneously stayed with moving the cursor to the area of the five hundredth stroke!
After a series of tests with the audio tracks on the network channels were activated by two MIDI-port. In this case, a more powerful computer were launched two software synthesizer, and served as a less powerful MIDI-sequencer and multitrack recorder. I must say that in this configuration, the network has been more or less stable. Trying to give all network channel for MIDI to fundamental improvements failed.
What is the cause of the identified network instability? In the “wet” technology or in a specific hardware configuration? To answer this question it would be good to hold another series of tests with a higher level of devices, for example, with the same cards RME. In the meantime, I note that the hardware and software configuration used during this test, it satisfies the requirements of the VST System Link. So personally, I’m leaning towards an embodiment of havoc with technology.
VST System Link: conclusions
So, taking as a basis the principle of the new technology, and not taking into account its current implementation, it is possible to talk about the next revolution in the music computer world. When properly constructed network of powerful computers and the use of quality-intensive plug-ins can be overcome basic “engineering” the lack of a virtual studio. Can finally be solved the problem with the lack of resources of one computer for high-quality mixing, processing and synthesis of sound.
However, we can not forget about the cost, which will result in the construction of such a network. Several powerful computers and sound cards with digital interface worth a lot, even if to do a single monitor, keyboard and mouse connected via KVM-switch. And that’s not to mention the cost of licensing the operating system on each computer, a licensed copy of the main program (the same on every computer) and on the cost of plug-ins, software synthesizers and samplers. As a result, the sum of the cost of the network virtual studio can catch up with the amount needed for the construction of the “iron” the studio with the same capabilities, and hardware implementation for all devices. Taking into account besides a rather complicated process of setting up and maintaining the health of a network version, I will refrain while giving predictions for its future. Time will tell.